Use JavaScript Optional Chaining, Today!
October 30, 2019
Optional Chaining is a new JavaScript API that will make developers' lives easier
In this article, I brief what is Optional Chaining, and why it's a game-changer. I will also try to guide you on how to configure it and use it. Let's get started.
Optional Chaining
If you already know what is Optional Chaining, you can skip the overview section, and head to the Configuration section.
Suppose you have a user, and you want to get its street address value.
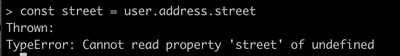
const street = user.address.street;
This code above will work fine if the user object exists and has the address property. But as you know the real-world scenarios are not that ideal. What if the user did not add his address yet. The JavaScript compiler will throw an error cannot read property street of undefined
To handle this issue and prevent compiler for throwing errors, I used to do something like this:
const street = user.address && user.address.street;
// or if need more than one value from address
const { address = {} } = user;
const street = address.street;
const country = address.country;
This seemed to be a good solution; but what if I want to access a deeply nested property, like user.subscription.attributes.name.en. It would be more challenging.
Here comes The Optional Chaining operator role, it allows you to optionally chain properties if it exists, without the need for assigning intermediate results in temporary variables:
const subscription = user.subscription?.attributes?.name?.en
Also if you want to set a default value you can use the proposed Nullish coalescing operator:
const animationDuration = response.settings?.animationDuration ?? 300;
The Optional Chaining can also optionally call a function if it exists:
myAwesomeFunction?.();
The first time I saw this syntax, it was very odd for me. But like any new syntax, I think it will take time until my eyes used to see it. you can read here why they had to use this syntax, for optionally calling functions.
Configuration
We can use Optional Chaining now throw the Babel compiler. I will describe how to configure:
Babel
Install @babel/plugin-proposal-optional-chaining
yarn add @babel/plugin-proposal-optional-chaining --dev
# or
npm install @babel/plugin-proposal-optional-chaining --save-dev
Add the plugin to .babelrc config file
{
"plugins": [
"@babel/plugin-proposal-optional-chaining"
]
}
ESLint
After you install the babel, you can use ?. optional chaining operator and Babel will compile it to the current working js. However, if you are using ESLint, it will not recognize the new syntax. We have to babel-eslint plugin in order to remove the eslint error.

yarn add babel-eslint --dev
# or
npm install babel-eslint --save-dev
Add .eslintrc config file
{
"parser": "babel-eslint",
"rules": {
"strict": 0
}
}
You can now test eslint is working fine, by running this command (make sure to install eslint globally).
eslint src/js/**
VS Code
The last part of this setup is to config VS Code editor, although ESLint is now aware of the optional chaining operator, you will notice that the VS Code is still displaying an annoying warning message.
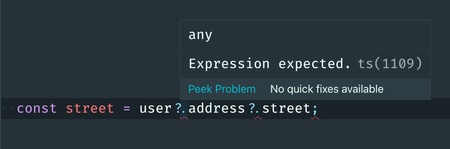
This is still an issue in VS Code validator, the workaround for this, we will have to disable the VS Code validator and work with ESLint extension.
First, make sure you have installed and active ESlint VS Code extension
Then add those configurations to the .vscode/settings.json file
{
"eslint.alwaysShowStatus": true,
"eslint.autoFixOnSave": true,
"javascript.validate.enable": false,
"[javascript]": {
"editor.formatOnSave": false,
},
"[javascriptreact]": {
"editor.formatOnSave": false,
},
// requires only if you use vetur plugin
"vetur.validation.script": false
}
Congratulations 🥳🥳, You are now using future technologies 👽👽.
If you have any questions, or you encounter difficulty in setup the configurations, you can post it in the comments section below. Happy Codding.
PS: Optional Changing Operator, is shipped in Chrome 78, and it's available now under Experimental JavaScript flag.